
system that to the ear, sounds like Baudot. 200 Hz Hertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). For example, the Russians use a 50 baud Baud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. There are many modes that sound like Baudot, but in fact aren't. Apart from occasional ham use, the only other known user is the Deutscher Wetterdienst (German Meteorological Service). Uses the ITA-2 alphabet (Commonly known as Baudot, derived from the Murray code). This mode is gradually dying out in favor of more robust modes like PSK31 in the amateur service. RTTY Radio TeleTYpe (Also known as Baudot or ITA2) uses the Baudot 5-bit alphabet with FSK Frequency-Shift Keying to send text messages over the shortwave. RTTY (Also known as Baudot or ITA2) uses the Baudot 5-bit alphabet with FSK to send text messages over the shortwave. In the 1980s, a large number of press agencies were still using radio teletype transmissions, but today radio amateurs and reports from weather radio services account for the majority of radio teletype transmissions. Click on the copy of the screen in order to listen to the corresponding audio signal.

In reality, only 50 and 75 bauds are available (in fact only 50 bauds). SITOR-B is an FEC method for transmission to different receivers. In commercial RTTY, the transmission speed may be, theoretically, 50, 75 or 100 bauds with a 85, 425 Hz, 450 or 850 Hz shift. RTTY transmissions on LF and VLF frequencies use a narrow shift of 85 Hz, due to the limited bandwidth of the antennas. Russian (and in the past, Soviet Union) merchant marine communications use 50 baud - 170 Hz. FEC-COL - Transmissions are directed „to all“, FEC-SEL is directed to a single remote station equipped with a selective call system. Commercial, diplomatic and weather services prefer 50 baud - 425 or 450 Hz, although few of them remain active in this mode. Here, characters are transmitted twice and a check bit allows error correction without the need for feedback to the transmitting station and thus a two-way communication / duplex connection.
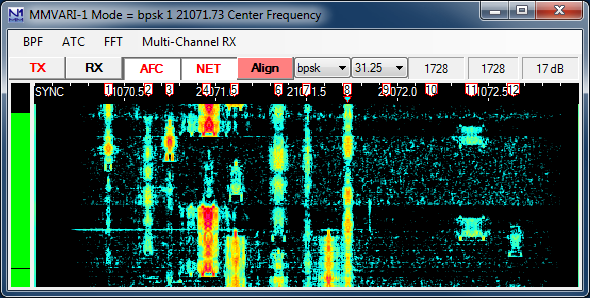
Technically, the FEC („Forward Error Correction“) mode differs significantly. The center of the radio receiver pass band (displayed on the waterfall) is at the offset frequency 1500 Hz. He has also successfully used a Yaesu 857D radio, which has only wider filters. With the SITOR-A method, an acknowledgement signal is expected from the remote receiving station only after the transmission of a block of three characters, which significantly increases the transmission speed while maintaining the same reliability in amateur radio, AMTOR-A („Amateur Microprocessor Teleprinter Over Radio“) is used as an equivalent. He prefers a 100 Hz wide filter setting on the Icom 7000 for PSK31 and 250 Hz for RTTY.
#Commercial rtty frequencies code#
This code is mainly known from its use in electronic data processing.įurther developments to the usual Baudot transmission mode were the ARQ procedures: Error-correcting transmission modes in which acknowledgement characters or repeat requests (RQ) are returned from the receiving station to the transmitter site. The ASCII code includes letters in upper and lower case, numbers and some special characters. The speed measured in baud (bit/sec.), the frequency shift (distance between the two tone frequencies, usually 170, 425 or 850 Hz) and the correct phase (whether „Mark“ or „Space“ is assigned to the lower of the two frequencies) has be set on the decoder.ĪSCII transmissions were only rarely used on shortwaves. With this two-tone mode (signal level „1“ or „Mark“ and signal level „0“ or „Space“), several paramters have to be set correctly on the decoder. In the eighties, automatic decoders became available: These could decode the text of a morse code or radio teletype transmission and display it on a monitor or a simple domestic television set.Ī contemporary radioteletype receiving system consists of a shortwave receiver with sufficient stability and capability for SSB reception, a decoder and a monitor, and possibly a printer for printing out the received message.įor radioteletype ( RTTY), usually the Baudot code (CCITT No. In the sixties, for the reception of Radio teletype ( RTTY) signals, not only a powerful shortwave receiver was needed, but also a FSK converter connected to a noisy rattling electric teletypewriter was needed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
